Last updated: 20 August 2022
This IoT post will show you how to control a wi-fi enabled chip using a mobile phone over MQTT.
For this demo we'll create a mobile app that takes a photo on an IoT device and displays it on the phone; but you can modify it to do other things (turn on a light, open a door, control a robot, respond to a sensor alert, for example).
We'll use an ESP32 cam AI Thinker board with an OV2640 camera as our remote device.
The example app is a simple Android application written in Java (although you can achieve the same goal using other languages and platforms).
Also bear in mind that this is simply a minimalist demonstration. There are many variations and optimisations that we can apply to this project.
Contents
- Stuff you'll need
- Logic overview
- Workflow
-
Steps
- Set up MQTT broker for IoT communication
- Create folder on FTP server for uploaded photos
- Set up OV2640 camera on AI Thinker ESP32 Cam board
- Wire USB-TTL adapter and ESP32 AI Thinker board for uploading code
- Code the ESP32
- Upload the ESP32 Cam code
- Code the Android App
- Take a Photo from your Phone using MQTT!
Stuff you'll need
(includes paid links)
- ESP32 Cam AI Thinker board (including OV2640 Camera)
- USB to TTL serial adapter (also ubiquitously referred to as "FTDI programmer" for some reason)
- 5 female-to-female jumper wires
- USB extension lead type A male-to-female (optional but more convenient than connecting the USB/serial adapter directly into the PC port)
- Access to an MQTT broker (internet or local)
- Read and write access to an FTP server (internet or local)
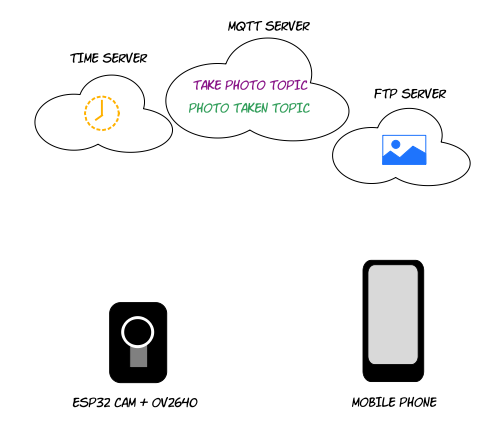
Logic overview
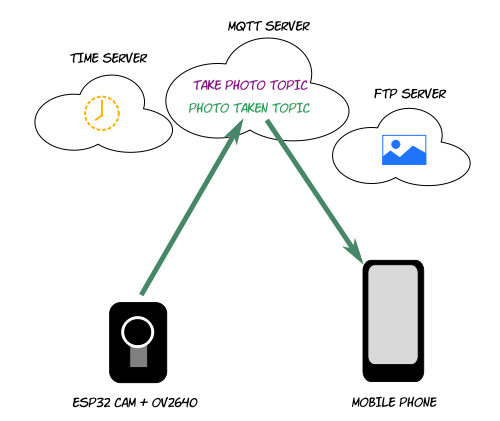
Architecture
The process involves MQTT 2 topics (check this post to learn how set this up). The ESP32 chip subscribes to the "take photo" topic to receive commands from the phone and the phone subscribes to the "photo taken" topic to receive notifications from the chip.
The ESP32 uploads the photos to the FTP server and the mobile app downloads them from the FTP server. The chip must have FTP write permission. The phone doesn't need FTP permissions for this simple example; it will download the photos via HTTP.
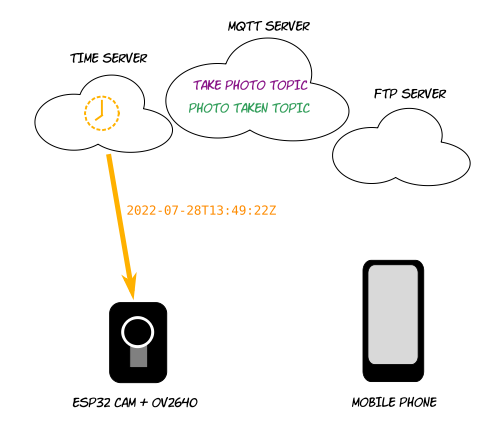
The time server is optional but ideal. It provides a timestamp to the ESP32 in order to generate a unique and meaningful filename for each photo (remember that, unlike your PC, the ESP32 chip has no idea what day or time it is). Including a timestamp in your filenames also makes it possible to list and display photos in chronological order.
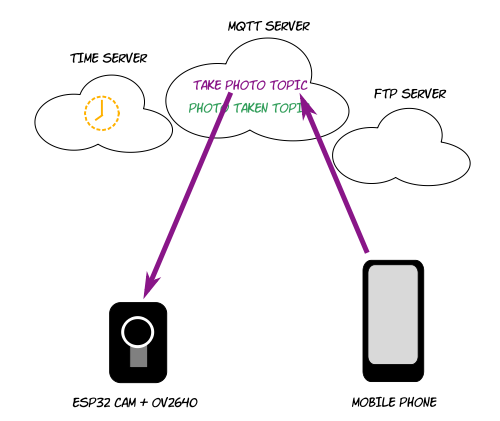
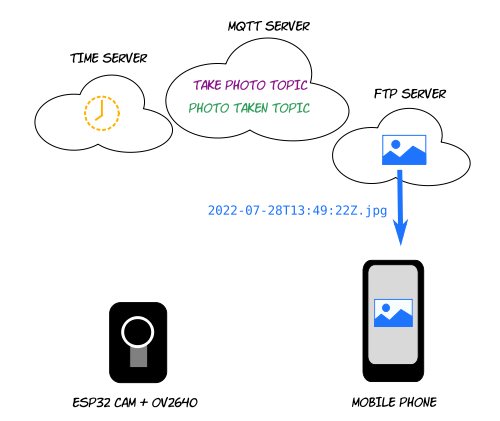
Workflow
Phone publishes to "take photo" topic; ESP32 receives message
ESP32 gets timestamp from date server to create filename
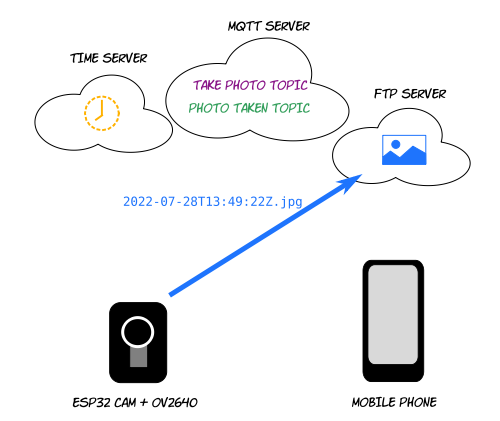
ESP32 takes photo, generates jpeg and uploads it to FTP server
ESP32 publishes notification to "photo taken" topic; phone receives notification
Mobile phone downloads photo by HTTP
Steps
Set up MQTT broker for IoT communication
MQTT broker set-up is explained here.
Create folder on FTP server for uploaded photos
The ESP32 chip needs FTP write permission; the mobile phone in this example doesn't need FTP permission.
Set up OV2640 camera on AI Thinker ESP32 Cam board
-
Open the ESP32 Cam FPCFlexible printed circuit connector on the AI Thinker
board by pulling it up gently with your finger (it's
easier than it looks!).
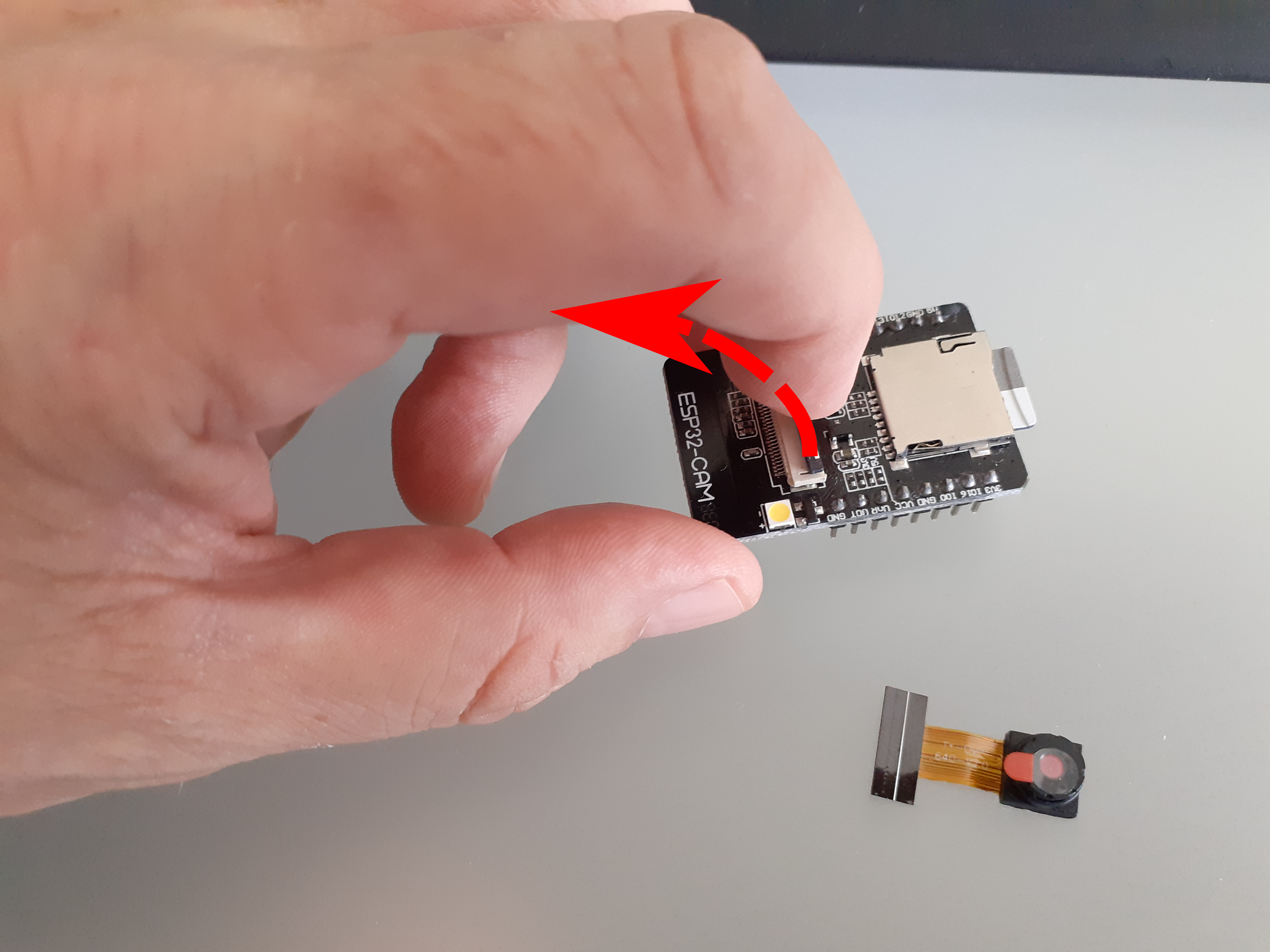
How to open the AI Thinker FPC camera connector -
Place the OV2640 camera into the FPC connector (also easier than it looks!).
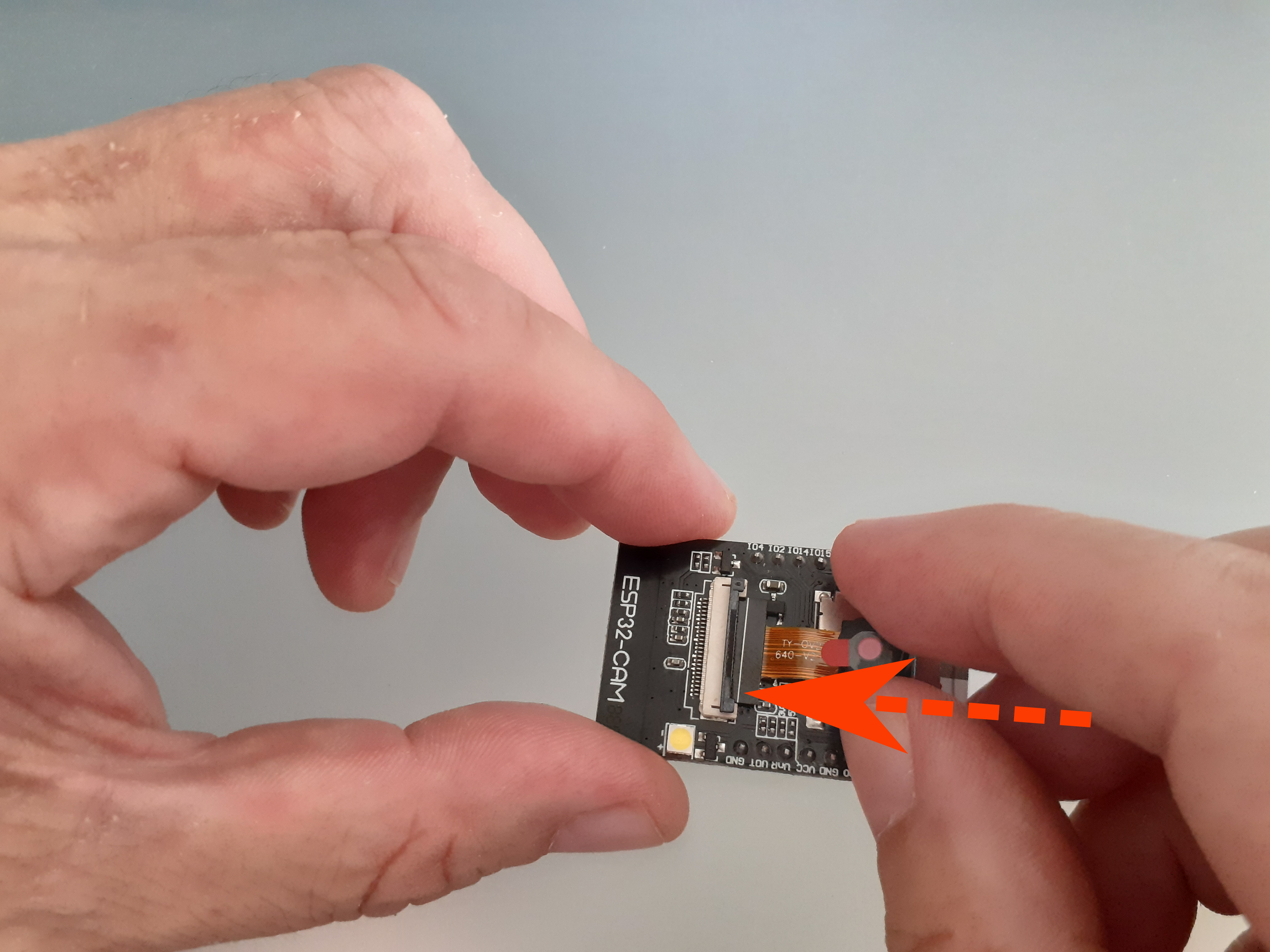
How to place the OV2640 camera into the AI Thinker FPC connector -
Close the AI Thinker FPC connector by pushing it down gently.
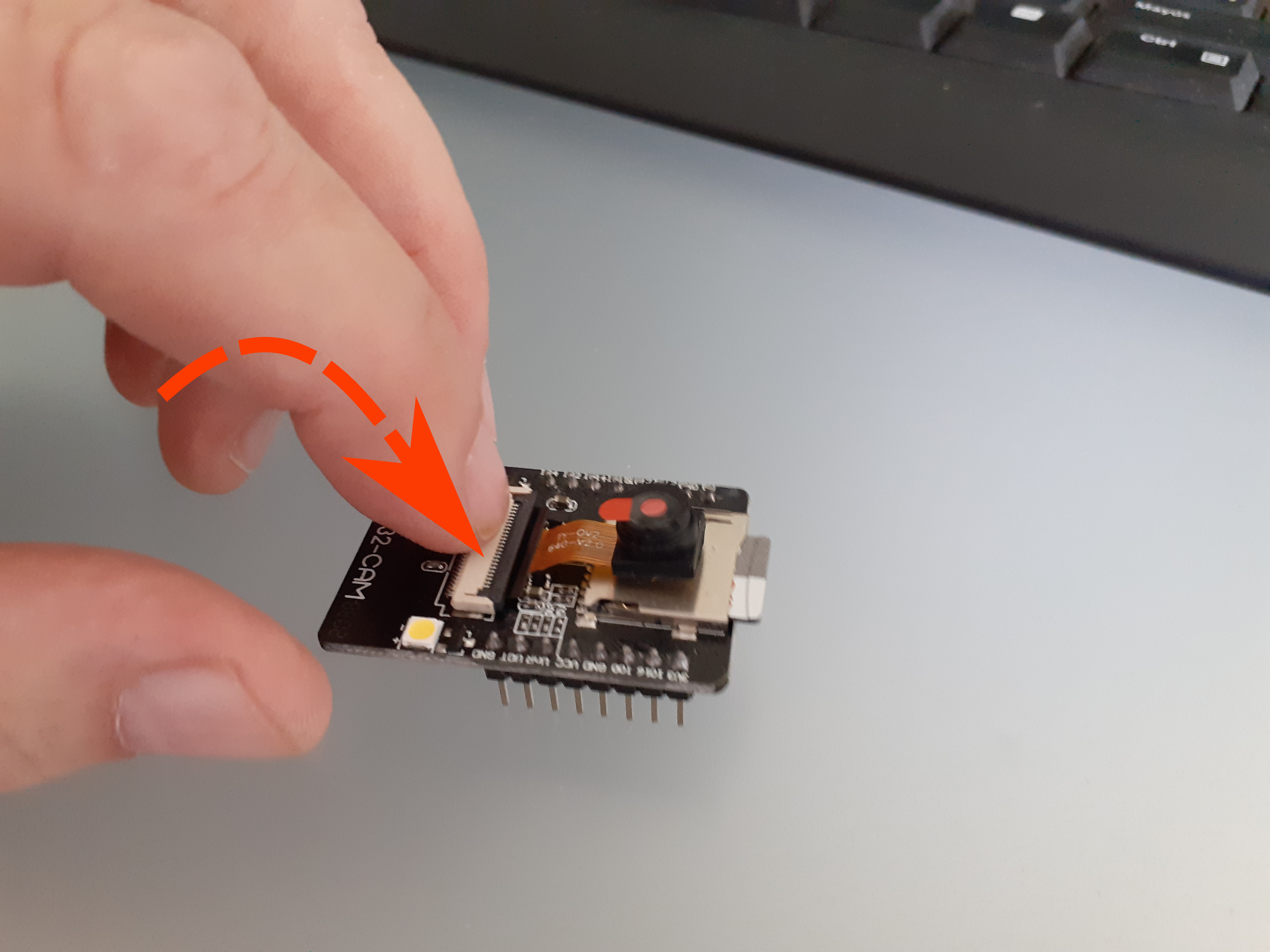
How to close the AI Thinker FPC camera connector - Don't forget to take the protective plastic off the OV2640 lens if it's brand new!
Wire USB-TTL adapter and ESP32 AI Thinker board for uploading code
Connect the USB-TTL adapter to your PC using a USB type A extension cable (you can also the dangle the adapter directly from one of the PCs USB ports but this is not so convenient and will severely limit what you can point the camera at); then connect the adapter to the AI Thinker ESP32 board.
The pin-to-pin mapping is as follows:
| USB/TTL adapter chip | AI Thinker ESP32-CAM board |
|---|---|
| 5v | 5v |
| GND | GND |
| TX | U0R |
| RX | U0T |
| Io0 - GND * |
* You need to short GPIO 0 pin to GND during upload (not when your code is running). Alternatively you can connect GPIO 0 to the second GND pin of the USB/TTL adapter if you prefer.
Schematic
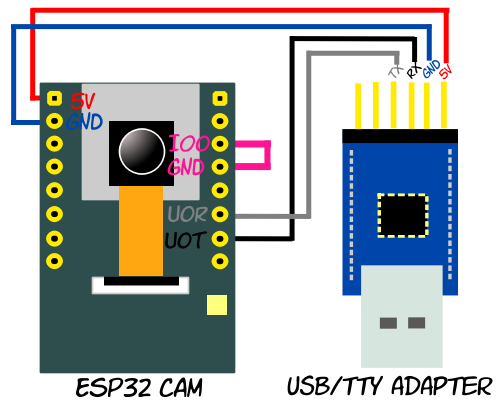
IMPORTANT - Check the labels of the pins of your USB/TTL adapter. The order isn't universal and could very easily be different from the model shown here. Make sure you identify 5v, GND, RX and TX correctly.
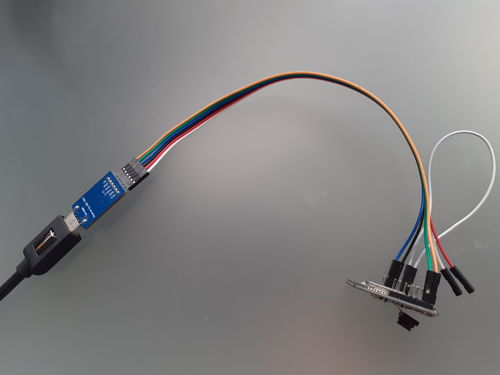
You should now be looking at something like this (note the white wire shorting GPIO0 to GND):
Code the ESP32
Open the Arduino IDE, create a new sketch and add the code. Let's go through it step-by-step (the complete code is shown further down this page):
Include the following libraries. If any are missing,
simply search for them in Tools >
Manage Libraries and click
Install. In the case that
a library is not available in the library manager,
search for the source on the internet, download the
zip, decompress it in your Arduino libraries folder
and restart the IDE.
#include "esp_camera.h" #include "soc/soc.h" // Needed to manage brown-out detection (which we'll disable) #include "soc/rtc_cntl_reg.h" // Needed to manage brown-out detection (which we'll disable) #include "driver/rtc_io.h" #include <WiFi.h> #include "ESP32_FTPClient.h" #include <WiFiClientSecure.h> #include <PubSubClient.h> // MQTT lib by knolleary (https://github.com/knolleary/pubsubclient) #include <NTPClient.h> #include <WiFiUdp.h> #include "time.h" #include "ArduinoJson.h" // JSON lib by Benoit Blanchon (https://www.arduinolibraries.info/libraries/arduino-json)
Add the connection parameters for your FTP server plus the URL and path which we'll send to the mobile phone each time we take a photo.
/* Parameters for FTP server connection */ char* FTP_URL = "ftp.your.ftpserver"; char* FTP_USER = "your@ftpuser"; char* FTP_PWD = "your ftp password"; char* FTP_PATH = "/path/to/photos/folder/"; /* Parameters for HTTP connection (so subscribers can download the images) */ char* HTTP_PATH = "https://URL/and/path/to/photos/folder/";
Add the parameters for the MQTT broker connection including the topic names and a prefix for the connection ID. This example uses Hive MQTT (see here to set that up) but feel free to use another broker.
/* Parameters for Hive MQTT connection*/ const char* MQTT_SERVER = "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx.s1.eu.hivemq.cloud"; const char* MQTT_USERNAME = "your MQTT username"; const char* MQTT_PWD = "your MQTT password"; const int MQTT_PORT = 8883; const char* MQTT_PUB_TOPIC = "yourtopics/photoTaken"; // we'll publish notifications to this topic each time we take a photo const char* MQTT_SUB_TOPIC = "yourtopics/takePhoto"; // we'll receive commands to take a photo from this topic const char* MQTT_CLIENT_ID_PREFIX = "some.prefix."; const int QOS = 1;
Add the keys we will use in the JSON payloads of our MQTT messages and a unique ID for our ESP32 Cam chip. These are all optional but will allow us to use multiple cameras and phones. Note that you will have to hardcode a unique SENSOR_ID value for each ESP32 Cam that you set up. Give it a meaningful name ("kitchen", "garden", "catflap" etc). This one is called "musicRoom".
/* JSON payload keys */ const char* SENSOR_ID_KEY = "sensorId"; // The key in the JSON payload for the sensor ID (used for publishing and receiving messages) const char* REQUESTOR_ID_KEY = "requestorId"; // The key in the JSON payload for the requestor device ID (used for publishing and receiving messages) const char* PHOTO_URL_KEY = "photo"; // The key in the JSON payload for the URL of uploaded photos /* The ID of this ESP32 cam device (we will ignore messages that aren't targeted at this ID) */ const char* SENSOR_ID = "musicRoom";
Add the parameters for your wifi router.
/* Parameters for WIFI connection */ const char* SSID = "your wifi SSID"; const char* WIFI_PWD = "your wifi password";
constants for filename convention
/* filename convention */ const char* FILE_EXTENSION = ".jpg"; // extension (always JPEG) const String FILENAME_SANITISER = "-"; // to delimit parts of filenames
Root certificate for secure connection to Hive MQTT (if you are using some other broker you won't need this).
/* Hive MQTT Root certificate */ static const char* ROOT_CA PROGMEM = R"EOF( -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- MIIFazCCA1OgAwIBAgIRAIIQz7DSQONZRGPgu2OCiwAwDQYJKoZIhvcNAQELBQAw TzELMAkGA1UEBhMCVVMxKTAnBgNVBAoTIEludGVybmV0IFNlY3VyaXR5IFJlc2Vh cmNoIEdyb3VwMRUwEwYDVQQDEwxJU1JHIFJvb3QgWDEwHhcNMTUwNjA0MTEwNDM4 WhcNMzUwNjA0MTEwNDM4WjBPMQswCQYDVQQGEwJVUzEpMCcGA1UEChMgSW50ZXJu ZXQgU2VjdXJpdHkgUmVzZWFyY2ggR3JvdXAxFTATBgNVBAMTDElTUkcgUm9vdCBY MTCCAiIwDQYJKoZIhvcNAQEBBQADggIPADCCAgoCggIBAK3oJHP0FDfzm54rVygc h77ct984kIxuPOZXoHj3dcKi/vVqbvYATyjb3miGbESTtrFj/RQSa78f0uoxmyF+ 0TM8ukj13Xnfs7j/EvEhmkvBioZxaUpmZmyPfjxwv60pIgbz5MDmgK7iS4+3mX6U A5/TR5d8mUgjU+g4rk8Kb4Mu0UlXjIB0ttov0DiNewNwIRt18jA8+o+u3dpjq+sW T8KOEUt+zwvo/7V3LvSye0rgTBIlDHCNAymg4VMk7BPZ7hm/ELNKjD+Jo2FR3qyH B5T0Y3HsLuJvW5iB4YlcNHlsdu87kGJ55tukmi8mxdAQ4Q7e2RCOFvu396j3x+UC B5iPNgiV5+I3lg02dZ77DnKxHZu8A/lJBdiB3QW0KtZB6awBdpUKD9jf1b0SHzUv KBds0pjBqAlkd25HN7rOrFleaJ1/ctaJxQZBKT5ZPt0m9STJEadao0xAH0ahmbWn OlFuhjuefXKnEgV4We0+UXgVCwOPjdAvBbI+e0ocS3MFEvzG6uBQE3xDk3SzynTn jh8BCNAw1FtxNrQHusEwMFxIt4I7mKZ9YIqioymCzLq9gwQbooMDQaHWBfEbwrbw qHyGO0aoSCqI3Haadr8faqU9GY/rOPNk3sgrDQoo//fb4hVC1CLQJ13hef4Y53CI rU7m2Ys6xt0nUW7/vGT1M0NPAgMBAAGjQjBAMA4GA1UdDwEB/wQEAwIBBjAPBgNV HRMBAf8EBTADAQH/MB0GA1UdDgQWBBR5tFnme7bl5AFzgAiIyBpY9umbbjANBgkq hkiG9w0BAQsFAAOCAgEAVR9YqbyyqFDQDLHYGmkgJykIrGF1XIpu+ILlaS/V9lZL ubhzEFnTIZd+50xx+7LSYK05qAvqFyFWhfFQDlnrzuBZ6brJFe+GnY+EgPbk6ZGQ 3BebYhtF8GaV0nxvwuo77x/Py9auJ/GpsMiu/X1+mvoiBOv/2X/qkSsisRcOj/KK NFtY2PwByVS5uCbMiogziUwthDyC3+6WVwW6LLv3xLfHTjuCvjHIInNzktHCgKQ5 ORAzI4JMPJ+GslWYHb4phowim57iaztXOoJwTdwJx4nLCgdNbOhdjsnvzqvHu7Ur TkXWStAmzOVyyghqpZXjFaH3pO3JLF+l+/+sKAIuvtd7u+Nxe5AW0wdeRlN8NwdC jNPElpzVmbUq4JUagEiuTDkHzsxHpFKVK7q4+63SM1N95R1NbdWhscdCb+ZAJzVc oyi3B43njTOQ5yOf+1CceWxG1bQVs5ZufpsMljq4Ui0/1lvh+wjChP4kqKOJ2qxq 4RgqsahDYVvTH9w7jXbyLeiNdd8XM2w9U/t7y0Ff/9yi0GE44Za4rF2LN9d11TPA mRGunUHBcnWEvgJBQl9nJEiU0Zsnvgc/ubhPgXRR4Xq37Z0j4r7g1SgEEzwxA57d emyPxgcYxn/eR44/KJ4EBs+lVDR3veyJm+kXQ99b21/+jh5Xos1AnX5iItreGCc= -----END CERTIFICATE----- )EOF";
Define ESP32 Cam pin numbers for the OV2640 camera and declare the camera configuration.
/* These values are for CAMERA_MODEL_AI_THINKER (copied from camera_pins.h in the Arduino CameraWebServer example) */ #define PWDN_GPIO_NUM 32 #define RESET_GPIO_NUM -1 #define XCLK_GPIO_NUM 0 #define SIOD_GPIO_NUM 26 #define SIOC_GPIO_NUM 27 #define Y9_GPIO_NUM 35 #define Y8_GPIO_NUM 34 #define Y7_GPIO_NUM 39 #define Y6_GPIO_NUM 36 #define Y5_GPIO_NUM 21 #define Y4_GPIO_NUM 19 #define Y3_GPIO_NUM 18 #define Y2_GPIO_NUM 5 #define VSYNC_GPIO_NUM 25 #define HREF_GPIO_NUM 23 #define PCLK_GPIO_NUM 22 camera_config_t cameraCfg; // Camera config (we'll apply the previous constants to this)
NTPnetwork time protocol connection parameters. We only need this to name the uploaded files. Here we're using the default WiFiUDP library configuration:
| parameter | value |
|---|---|
| server | pool.ntp.org |
| timezone offset | 0 (ie. UTC) |
| update interval | 60000 (ie. each minute) |
You can parameterise the connection as you prefer (more information at the NTPClient gitub repo). For example:
NTPClient ntpClient(ntpUDP, "europe.pool.ntp.org", (3600*2), 30000);
NTPClient ntpClient(ntpUDP);
Start the FTP session.
ESP32_FTPClient ftp (FTP_URL, FTP_USER, FTP_PWD, 5000, 2);
Instantiate the wifi client and the MQTT client.
WiFiClientSecure espClient; PubSubClient mqttClient(espClient);
Add a function to start the wifi connection, which we'll call from our setup() function.
void setupWifi() {
delay(10);
Serial.print("\nConnecting to ");
Serial.println(SSID);
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA);
WiFi.begin(SSID, WIFI_PWD);
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.print("\nWiFi connected\nIP address: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
}
Add a function to start the OV2649 camera, which we'll call from our setup() function.
void setupCamera() {
cameraCfg.ledc_channel = LEDC_CHANNEL_0;
cameraCfg.ledc_timer = LEDC_TIMER_0;
cameraCfg.pin_d0 = Y2_GPIO_NUM;
cameraCfg.pin_d1 = Y3_GPIO_NUM;
cameraCfg.pin_d2 = Y4_GPIO_NUM;
cameraCfg.pin_d3 = Y5_GPIO_NUM;
cameraCfg.pin_d4 = Y6_GPIO_NUM;
cameraCfg.pin_d5 = Y7_GPIO_NUM;
cameraCfg.pin_d6 = Y8_GPIO_NUM;
cameraCfg.pin_d7 = Y9_GPIO_NUM;
cameraCfg.pin_xclk = XCLK_GPIO_NUM;
cameraCfg.pin_pclk = PCLK_GPIO_NUM;
cameraCfg.pin_vsync = VSYNC_GPIO_NUM;
cameraCfg.pin_href = HREF_GPIO_NUM;
cameraCfg.pin_sscb_sda = SIOD_GPIO_NUM;
cameraCfg.pin_sscb_scl = SIOC_GPIO_NUM;
cameraCfg.pin_pwdn = PWDN_GPIO_NUM;
cameraCfg.pin_reset = RESET_GPIO_NUM;
cameraCfg.xclk_freq_hz = 20000000;
cameraCfg.pixel_format = PIXFORMAT_JPEG;
// Configure modest image proportions and quality to save memory, bandwidth, server space and speed up process (sufficient for this demo)
cameraCfg.frame_size = FRAMESIZE_SVGA;
cameraCfg.jpeg_quality = 12;
cameraCfg.fb_count = 1;
// Start camera
esp_err_t status = esp_camera_init(&cameraCfg);
if (status != ESP_OK) {
Serial.printf("Could not start camera: error code 0x%x", status);
return;
}
}
Add a function to connect to the MQTT broker, which we'll call from our setup() function.
void connectMQTT() {
randomSeed(micros());
Serial.println("Checking MQTT connection...");
while (!mqttClient.connected()) {
Serial.println("Connecting to MQTT broker...");
String clientId = MQTT_CLIENT_ID_PREFIX + String(random(0xffff), HEX);
if (mqttClient.connect(clientId.c_str(), MQTT_USERNAME, MQTT_PWD)) {
Serial.println("MQTT connected");
mqttClient.subscribe(MQTT_SUB_TOPIC, QOS);
} else {
Serial.println("Error connecting to " + mqttClient.state());
delay(5000);
}
}
}
Create a callback function that will be
called by the PubSub object each time some other
client publishes a message to the takePhoto
topic. The code deserialises the incoming JSON
message, extracts the target sensorID and the ID
of the device that requested the photo. If the
SENSOR_ID_KEY in the JSON payload matches our
SENSOR_ID, we'll take and upload a photo. We'll
include the requestor ID in the notification
to the photoTaken topic so that each
mobile device knows whether it requested the
photo. This is redundant, of course, if you
are only connecting from a single mobile phone. The
callback() function also
refreshes the timestamp from the NTP server and
initiates the photo capture and FTP upload.
void callback(char* topic, byte* payload, unsigned int length){
Serial.println("callback() invoked");
StaticJsonDocument<200> json;
DeserializationError jsonError = deserializeJson(json, payload);
if (jsonError) {
Serial.print(F("deserializeJson() failed: "));
Serial.println(jsonError.f_str());
return;
}
const char* sensorId = json[SENSOR_ID_KEY];
const char* requestorId = json[REQUESTOR_ID_KEY];
Serial.print("sensor: ");
Serial.println(sensorId);
Serial.print("requestor ID: ");
Serial.println(requestorId);
ntpClient.update();
camera_fb_t * fb = takePhoto();
uploadPhoto(fb, requestorId);
esp_camera_fb_return(fb);
Serial.println("Photo taken");
}
Create a function to take
a photo and return the image data in JPEG
format. This function will be called by our
callback() method.
/* Take a photo and return the image data as a Frame Buffer object*/
camera_fb_t * takePhoto() {
camera_fb_t * fb = NULL;
fb = esp_camera_fb_get();
if(!fb) {
Serial.println("Couldn't take photo!!!!");
}
return fb;
}
Create a method to name the JPEG file, upload it to the FTP server, generate and publish the notification message to the photoTaken topic. The JSON payload of the message will contain the ID of the ESP32 Cam, the ID of the mobile phone that requested the photo and the HTTP URL of the file that has been uploaded by FTP. Note that you can modify the Android code to download via FTP if you prefer.
void uploadPhoto(camera_fb_t * fb, const char* requestorId){
Serial.println("Uploading image by FTP...");
Serial.println("Starting FTP session..");
ftp.OpenConnection();
Serial.println("FTP session started");
ftp.ChangeWorkDir(FTP_PATH);
ftp.InitFile("Type I");
String filename = SENSOR_ID + FILENAME_SANITISER + ntpClient.getFormattedDate() + FILE_EXTENSION;
int l = filename.length() + 1;
char dst[l];
filename.toCharArray(dst, l);
Serial.print("File name: ");
Serial.println(dst) ;
ftp.NewFile(dst);
ftp.WriteData(fb->buf, fb->len);
ftp.CloseFile();
ftp.CloseConnection();
if (!mqttClient.connected()) {
Serial.println("MQTT not connected. Connecting now...");
connectMQTT(); // connect to the MQTT broker if not connected
}
else{
Serial.println("MQTT already connected");
}
Serial.print("Publishing message: ");
Serial.print(dst);
Serial.print(" to topic: ");
Serial.print(MQTT_PUB_TOPIC);
Serial.println("...");
char httpURL[strlen(HTTP_PATH) + strlen(dst)]; // array to hold the complete HTTP URL to the image we've just uploaded
strcpy(httpURL, HTTP_PATH); // add the domain to the URL.
strcat(httpURL, dst); // append the path to the URL
StaticJsonDocument<200> json;
json[SENSOR_ID_KEY] = SENSOR_ID;
json[REQUESTOR_ID_KEY] = requestorId;
json[PHOTO_URL_KEY] = httpURL;
int payloadSize = measureJson(json) + 1;
char payload[payloadSize];
serializeJson(json, payload, sizeof(payload));
mqttClient.publish(MQTT_PUB_TOPIC, payload, true);
Serial.println("Message published");
}
Code the ESP32 Cam setup()
method (which runs once each time you reset the chip) to set up
serial communication (for debugging), the wifi connection, the camera,
the NTP server connection and the MQTT server connection.
Note also that this method disables brown-out detection, meaning that the ESP32 Cam will not reset itself each time there is drop in voltage.
void setup() {
WRITE_PERI_REG(RTC_CNTL_BROWN_OUT_REG, 0); // Disable brown-out detector
Serial.begin(115200);
setupWifi();
setupCamera();
ntpClient.begin();
espClient.setCACert(ROOT_CA); // set the cert for the MQTT conection
mqttClient.setServer(MQTT_SERVER, MQTT_PORT); // set the params for the server
mqttClient.setCallback(callback); // set the callback function that will run each time we receive an MQTT message
}
The loop() function
(which the ESP32 Cam calls repeatedly at runtime)
ensures we stay connected to the MQTT server and
that our session does not expire.
void loop() {
if (!mqttClient.connected()) {
connectMQTT();
}
mqttClient.loop(); // call the MQTT client's keepalive function
}
The complete ESP32 Cam code
#include "esp_camera.h"
#include "soc/soc.h" // Needed to manage brown-out detection (which we'll disable)
#include "soc/rtc_cntl_reg.h" // Needed to manage brown-out detection (which we'll disable)
#include "driver/rtc_io.h"
#include <WiFi.h>
#include "ESP32_FTPClient.h"
#include <WiFiClientSecure.h>
#include <PubSubClient.h> // MQTT lib by knolleary (https://github.com/knolleary/pubsubclient)
#include <NTPClient.h>
#include <WiFiUdp.h>
#include "time.h"
#include "ArduinoJson.h" // JSON lib by Benoit Blanchon (https://www.arduinolibraries.info/libraries/arduino-json)
/* Parameters for FTP server connection */
char* FTP_URL = "ftp.your.ftpserver";
char* FTP_USER = "your@ftpuser";
char* FTP_PWD = "your ftp password";
char* FTP_PATH = "/path/to/photos/folder/";
/* Parameters for HTTP connection (so subscribers can download the images) */
char* HTTP_PATH = "https://URL/and/path/to/photos/folder/";
/* Parameters for Hive MQTT connection*/
const char* MQTT_SERVER = "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx.s1.eu.hivemq.cloud";
const char* MQTT_USERNAME = "your MQTT username";
const char* MQTT_PWD = "your MQTT password";
const int MQTT_PORT = 8883;
const char* MQTT_PUB_TOPIC = "yourtopics/photoTaken"; // we'll publish notifications to this topic each time we take a photo
const char* MQTT_SUB_TOPIC = "yourtopics/takePhoto"; // we'll receive commands to take a photo from this topic
const char* MQTT_CLIENT_ID_PREFIX = "some.prefix.";
const int QOS = 1;
/* JSON payload keys */
const char* SENSOR_ID_KEY = "sensorId"; // The key in the JSON payload for the sensor ID (used for publishing and receiving messages)
const char* REQUESTOR_ID_KEY = "requestorId"; // The key in the JSON payload for the requestor device ID (used for publishing and receiving messages)
const char* PHOTO_URL_KEY = "photo"; // The key in the JSON payload for the URL of uploaded photos
/* The ID of this ESP32 cam device (we will ignore messages that aren't targeted at this ID) */
const char* SENSOR_ID = "musicRoom";
/* Parameters for WIFI connection */
const char* SSID = "your wifi SSID";
const char* WIFI_PWD = "your wifi password";
/* filename convention */
const char* FILE_EXTENSION = ".jpg"; // extension (always JPEG)
const String FILENAME_SANITISER = "-"; // to delimit parts of filenames
/* Hive MQTT Root certificate */
static const char* ROOT_CA PROGMEM = R"EOF(
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
MIIFazCCA1OgAwIBAgIRAIIQz7DSQONZRGPgu2OCiwAwDQYJKoZIhvcNAQELBQAw
TzELMAkGA1UEBhMCVVMxKTAnBgNVBAoTIEludGVybmV0IFNlY3VyaXR5IFJlc2Vh
cmNoIEdyb3VwMRUwEwYDVQQDEwxJU1JHIFJvb3QgWDEwHhcNMTUwNjA0MTEwNDM4
WhcNMzUwNjA0MTEwNDM4WjBPMQswCQYDVQQGEwJVUzEpMCcGA1UEChMgSW50ZXJu
ZXQgU2VjdXJpdHkgUmVzZWFyY2ggR3JvdXAxFTATBgNVBAMTDElTUkcgUm9vdCBY
MTCCAiIwDQYJKoZIhvcNAQEBBQADggIPADCCAgoCggIBAK3oJHP0FDfzm54rVygc
h77ct984kIxuPOZXoHj3dcKi/vVqbvYATyjb3miGbESTtrFj/RQSa78f0uoxmyF+
0TM8ukj13Xnfs7j/EvEhmkvBioZxaUpmZmyPfjxwv60pIgbz5MDmgK7iS4+3mX6U
A5/TR5d8mUgjU+g4rk8Kb4Mu0UlXjIB0ttov0DiNewNwIRt18jA8+o+u3dpjq+sW
T8KOEUt+zwvo/7V3LvSye0rgTBIlDHCNAymg4VMk7BPZ7hm/ELNKjD+Jo2FR3qyH
B5T0Y3HsLuJvW5iB4YlcNHlsdu87kGJ55tukmi8mxdAQ4Q7e2RCOFvu396j3x+UC
B5iPNgiV5+I3lg02dZ77DnKxHZu8A/lJBdiB3QW0KtZB6awBdpUKD9jf1b0SHzUv
KBds0pjBqAlkd25HN7rOrFleaJ1/ctaJxQZBKT5ZPt0m9STJEadao0xAH0ahmbWn
OlFuhjuefXKnEgV4We0+UXgVCwOPjdAvBbI+e0ocS3MFEvzG6uBQE3xDk3SzynTn
jh8BCNAw1FtxNrQHusEwMFxIt4I7mKZ9YIqioymCzLq9gwQbooMDQaHWBfEbwrbw
qHyGO0aoSCqI3Haadr8faqU9GY/rOPNk3sgrDQoo//fb4hVC1CLQJ13hef4Y53CI
rU7m2Ys6xt0nUW7/vGT1M0NPAgMBAAGjQjBAMA4GA1UdDwEB/wQEAwIBBjAPBgNV
HRMBAf8EBTADAQH/MB0GA1UdDgQWBBR5tFnme7bl5AFzgAiIyBpY9umbbjANBgkq
hkiG9w0BAQsFAAOCAgEAVR9YqbyyqFDQDLHYGmkgJykIrGF1XIpu+ILlaS/V9lZL
ubhzEFnTIZd+50xx+7LSYK05qAvqFyFWhfFQDlnrzuBZ6brJFe+GnY+EgPbk6ZGQ
3BebYhtF8GaV0nxvwuo77x/Py9auJ/GpsMiu/X1+mvoiBOv/2X/qkSsisRcOj/KK
NFtY2PwByVS5uCbMiogziUwthDyC3+6WVwW6LLv3xLfHTjuCvjHIInNzktHCgKQ5
ORAzI4JMPJ+GslWYHb4phowim57iaztXOoJwTdwJx4nLCgdNbOhdjsnvzqvHu7Ur
TkXWStAmzOVyyghqpZXjFaH3pO3JLF+l+/+sKAIuvtd7u+Nxe5AW0wdeRlN8NwdC
jNPElpzVmbUq4JUagEiuTDkHzsxHpFKVK7q4+63SM1N95R1NbdWhscdCb+ZAJzVc
oyi3B43njTOQ5yOf+1CceWxG1bQVs5ZufpsMljq4Ui0/1lvh+wjChP4kqKOJ2qxq
4RgqsahDYVvTH9w7jXbyLeiNdd8XM2w9U/t7y0Ff/9yi0GE44Za4rF2LN9d11TPA
mRGunUHBcnWEvgJBQl9nJEiU0Zsnvgc/ubhPgXRR4Xq37Z0j4r7g1SgEEzwxA57d
emyPxgcYxn/eR44/KJ4EBs+lVDR3veyJm+kXQ99b21/+jh5Xos1AnX5iItreGCc=
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
)EOF";
/* These values are for CAMERA_MODEL_AI_THINKER (copied from camera_pins.h in the Arduino CameraWebServer example) */
#define PWDN_GPIO_NUM 32
#define RESET_GPIO_NUM -1
#define XCLK_GPIO_NUM 0
#define SIOD_GPIO_NUM 26
#define SIOC_GPIO_NUM 27
#define Y9_GPIO_NUM 35
#define Y8_GPIO_NUM 34
#define Y7_GPIO_NUM 39
#define Y6_GPIO_NUM 36
#define Y5_GPIO_NUM 21
#define Y4_GPIO_NUM 19
#define Y3_GPIO_NUM 18
#define Y2_GPIO_NUM 5
#define VSYNC_GPIO_NUM 25
#define HREF_GPIO_NUM 23
#define PCLK_GPIO_NUM 22
camera_config_t cameraCfg; // Camera config (we'll apply the previous constants to this)
/* NTP (network time protocol) connection parameters
- we only need this to name the uploaded files */
WiFiUDP ntpUDP;
NTPClient ntpClient(ntpUDP); // defaults: server: pool.ntp.org; timezone offset: 0 (ie. UTC); update interval: 60000
// parameterised example: NTPClient ntpClient(ntpUDP, "europe.pool.ntp.org", (3600*2), 30000);
// Start the FTP session
ESP32_FTPClient ftp (FTP_URL, FTP_USER, FTP_PWD, 5000, 2);
WiFiClientSecure espClient;
PubSubClient mqttClient(espClient); // API available here: https://pubsubclient.knolleary.net/api#subscribe
void setupWifi() {
delay(10);
Serial.print("\nConnecting to ");
Serial.println(SSID);
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA);
WiFi.begin(SSID, WIFI_PWD);
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.print("\nWiFi connected\nIP address: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
}
void setupCamera() {
cameraCfg.ledc_channel = LEDC_CHANNEL_0;
cameraCfg.ledc_timer = LEDC_TIMER_0;
cameraCfg.pin_d0 = Y2_GPIO_NUM;
cameraCfg.pin_d1 = Y3_GPIO_NUM;
cameraCfg.pin_d2 = Y4_GPIO_NUM;
cameraCfg.pin_d3 = Y5_GPIO_NUM;
cameraCfg.pin_d4 = Y6_GPIO_NUM;
cameraCfg.pin_d5 = Y7_GPIO_NUM;
cameraCfg.pin_d6 = Y8_GPIO_NUM;
cameraCfg.pin_d7 = Y9_GPIO_NUM;
cameraCfg.pin_xclk = XCLK_GPIO_NUM;
cameraCfg.pin_pclk = PCLK_GPIO_NUM;
cameraCfg.pin_vsync = VSYNC_GPIO_NUM;
cameraCfg.pin_href = HREF_GPIO_NUM;
cameraCfg.pin_sscb_sda = SIOD_GPIO_NUM;
cameraCfg.pin_sscb_scl = SIOC_GPIO_NUM;
cameraCfg.pin_pwdn = PWDN_GPIO_NUM;
cameraCfg.pin_reset = RESET_GPIO_NUM;
cameraCfg.xclk_freq_hz = 20000000;
cameraCfg.pixel_format = PIXFORMAT_JPEG;
// Configure modest image proportions and quality to save memory, bandwidth, server space and speed up process (sufficient for this demo)
cameraCfg.frame_size = FRAMESIZE_SVGA;
cameraCfg.jpeg_quality = 12;
cameraCfg.fb_count = 1;
// Start camera
esp_err_t status = esp_camera_init(&cameraCfg);
if (status != ESP_OK) {
Serial.printf("Could not start camera: error code 0x%x", status);
return;
}
}
void connectMQTT() {
randomSeed(micros());
Serial.println("Checking MQTT connection...");
while (!mqttClient.connected()) {
Serial.println("Connecting to MQTT broker...");
String clientId = MQTT_CLIENT_ID_PREFIX + String(random(0xffff), HEX);
if (mqttClient.connect(clientId.c_str(), MQTT_USERNAME, MQTT_PWD)) {
Serial.println("MQTT connected");
mqttClient.subscribe(MQTT_SUB_TOPIC, QOS);
} else {
Serial.println("Error connecting to " + mqttClient.state());
delay(5000);
}
}
}
void callback(char* topic, byte* payload, unsigned int length){
Serial.println("callback() invoked");
StaticJsonDocument<200> json; // or DynamicJsonDocument json(200);
DeserializationError jsonError = deserializeJson(json, payload);
if (jsonError) {
Serial.print(F("deserializeJson() failed: "));
Serial.println(jsonError.f_str());
return;
}
const char* sensorId = json[SENSOR_ID_KEY];
const char* requestorId = json[REQUESTOR_ID_KEY];
Serial.print("sensor: ");
Serial.println(sensorId);
Serial.print("requestor ID: ");
Serial.println(requestorId);
ntpClient.update(); // call take-photo and upload functions
camera_fb_t * fb = takePhoto();
uploadPhoto(fb, requestorId);
esp_camera_fb_return(fb);
Serial.println("Photo taken");
}
/* Take a photo and return the image data as a Frame Buffer object*/
camera_fb_t * takePhoto() {
camera_fb_t * fb = NULL;
fb = esp_camera_fb_get();
if(!fb) {
Serial.println("Couldn't take photo!!!!");
}
return fb;
}
void uploadPhoto(camera_fb_t * fb, const char* requestorId){
Serial.println("Uploading image by FTP...");
Serial.println("Starting FTP session..");
ftp.OpenConnection();
Serial.println("FTP session started");
ftp.ChangeWorkDir(FTP_PATH);
ftp.InitFile("Type I");
String filename = SENSOR_ID + FILENAME_SANITISER + ntpClient.getFormattedDate() + FILE_EXTENSION;
int l = filename.length() + 1;
char dst[l];
filename.toCharArray(dst, l);
Serial.print("File name: ");
Serial.println(dst) ;
ftp.NewFile(dst);
ftp.WriteData(fb->buf, fb->len);
ftp.CloseFile();
ftp.CloseConnection();
if (!mqttClient.connected()) {
Serial.println("MQTT not connected. Connecting now...");
connectMQTT(); // connect to the MQTT broker if not connected
}
else{
Serial.println("MQTT already connected");
}
Serial.print("Publishing message: ");
Serial.print(dst);
Serial.print(" to topic: ");
Serial.print(MQTT_PUB_TOPIC);
Serial.println("...");
char httpURL[strlen(HTTP_PATH) + strlen(dst)]; // array to hold the complete HTTP URL to the image we've just uploaded
strcpy(httpURL, HTTP_PATH); // add the domain to the URL.
strcat(httpURL, dst); // append the path to the URL
StaticJsonDocument<200> json;
json[SENSOR_ID_KEY] = SENSOR_ID;
json[REQUESTOR_ID_KEY] = requestorId;
json[PHOTO_URL_KEY] = httpURL;
int payloadSize = measureJson(json) + 1;
char payload[payloadSize];
serializeJson(json, payload, sizeof(payload));
mqttClient.publish(MQTT_PUB_TOPIC, payload, true);
Serial.println("Message published");
}
void setup() {
WRITE_PERI_REG(RTC_CNTL_BROWN_OUT_REG, 0); // Disable brown-out detector
Serial.begin(115200);
setupWifi();
setupCamera();
ntpClient.begin();
espClient.setCACert(ROOT_CA); // set the cert for the MQTT conection
mqttClient.setServer(MQTT_SERVER, MQTT_PORT); // set the params for the server
mqttClient.setCallback(callback); // set the callback function that will run each time we receive an MQTT message
}
void loop() {
if (!mqttClient.connected()) {
connectMQTT();
}
mqttClient.loop(); // call the MQTT clients keepalive function
}
Upload the ESP32 Cam code
Follow these steps:
- Make sure the ESP32 Cam GPIO 0 pin is shorted to GND as explained above (either by connecting it to the GND pin on the ESP32 or directly to the second GND pin on the USB/TTL adapter).
- Reset the ESP32 by pressing the tiny reset button with your fingernail. You don't need to press hard. When the chip resets you will feel the button depress firmly and come back up. You will also see the flash LED light up.
Tools > Board, select AI Thinker ESP32-CAM.Tools > Port, select whichever USB port you are connected to.Tools > Serial Monitorand set the baud rate to115200(it needs to match the rate specified on this line in our ESP32 code:Serial.begin(115200))Sketch > Upload(orCtrl + U)- Disconnect GPIO0 from GND. IMPORTANT - If you don't do this, the ESP32 won't start!!!
Code the Android App
Set up a new Android Studio project
- Open Android Studio.
File > New > New Project.- Select
Empty Activity.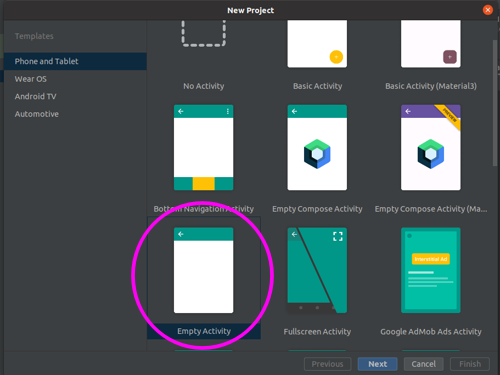
New Android project - Hit
Nextand- Give your project a name
- Create a package name (or just accept the default)
- Specify
Javaas the language - Hit
Finish
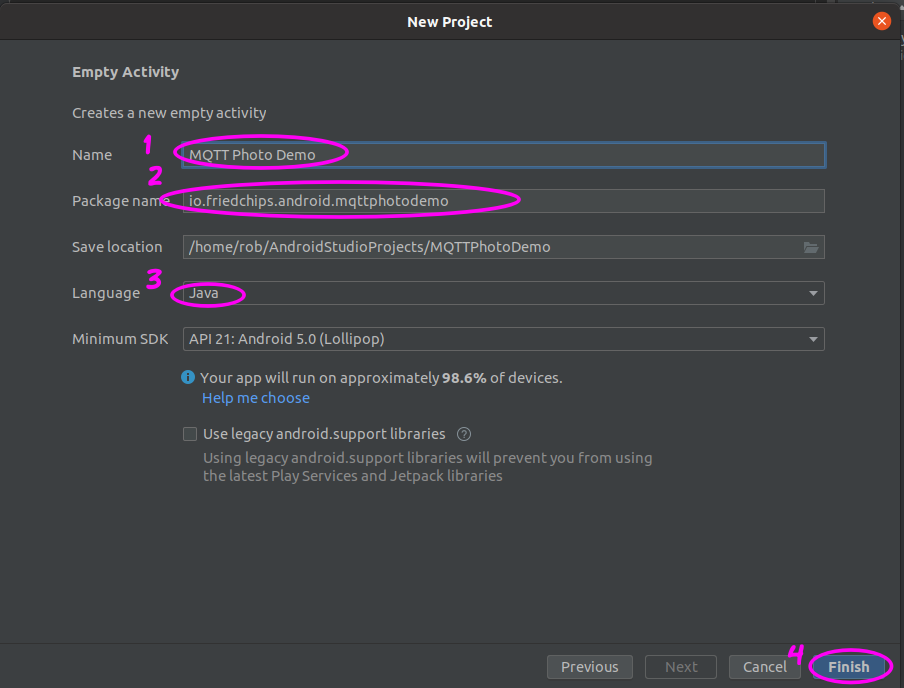
New Android project parameters -
Two tabs will appear in the IDE:
activity_main.xmlandMainActivity.java.activity_main.xmlcontains the components of our application andMainActivity.javacontains the logic.Select the
activity_main.xmltab and substitute all the default XML that was generated by the IDE for the following:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".MainActivity"> <ImageButton android:id="@+id/takeMusicRoomPhotoBtn" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginStart="0dp" android:layout_marginTop="28dp" android:onClick="takePhoto" android:tag="musicRoom" app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent" app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.0" app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" app:srcCompat="@android:drawable/ic_menu_camera" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/status" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Status pending..." android:layout_marginStart="0dp" app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent" app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent" app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0" app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" app:layout_constraintVertical_bias="0.162" /> <ImageView android:id="@+id/photoView" android:layout_width="377dp" android:layout_height="445dp" app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent" app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent" app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" app:layout_constraintVertical_bias="0.524" app:srcCompat="@android:drawable/ic_menu_camera" /> </androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>This gets us a button to take the photo, a text box to display the status of our MQTT calls and an android ImageView widget where our photos will appear.
Note the following:
- The
android:idvalues are important because our java code will need to point to these. - The ImageButton's
android:tagis "musicRoom" for this example. You can call it what you like, of course, but bear in mind that it must be exactly the same as the value defined hereconst char* SENSOR_ID = "musicRoom";in the ESP32 Cam code. If it is different, the ESP32 will disregard the MQTT message. This is so multiple cameras can subscribe to our takePhoto topic and we can add more buttons to our Android app. - The ImageButton's
android:onClick="takePhoto"property shows temporarily as an error (a red, wiggly line below the value). This is because thetakePhoto()method doesn't exist yet. We still need to write the Java code ;)
- The
Configure the Android manifest
Add the properties highlighted below to
manifests/AndroidManifest.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
package="io.friedchips.android.mqttphotodemo">
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WAKE_LOCK" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_PHONE_STATE" />
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:dataExtractionRules="@xml/data_extraction_rules"
android:fullBackupContent="@xml/backup_rules"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/Theme.MQTTPhotoDemo"
tools:targetApi="31">
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:exported="true">
android:configChanges="orientation|screenSize">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<service android:name="org.eclipse.paho.android.service.MqttService"></service>
</application>
</manifest>
Add dependencies to the Gradle build file
Add the dependencies highlighted below toapp/gradle.build:
plugins {
id 'com.android.application'
}
android {
compileSdk 32
defaultConfig {
applicationId "io.friedchips.android.mqttphotodemo"
minSdk 21
targetSdk 32
versionCode 1
versionName "1.0"
testInstrumentationRunner "androidx.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner"
}
buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled false
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android-optimize.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'
}
}
compileOptions {
sourceCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
targetCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
}
}
dependencies {
implementation 'androidx.appcompat:appcompat:1.4.2'
implementation 'com.google.android.material:material:1.6.1'
implementation 'androidx.constraintlayout:constraintlayout:2.1.4'
implementation 'com.squareup.picasso:picasso:2.71828'
implementation 'org.eclipse.paho:org.eclipse.paho.client.mqttv3:1.2.2'
implementation 'org.eclipse.paho:org.eclipse.paho.android.service:1.0.2'
testImplementation 'junit:junit:4.13.2'
androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test.ext:junit:1.1.3'
androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test.espresso:espresso-core:3.4.0'
}
Now import those dependencies into the Android project by
hitting Sync Project with Gradle Files
in the Android Studio menu bar.
In the activity_main.xml tab click
on the Design view (1)
to see a visual representation of the layout.
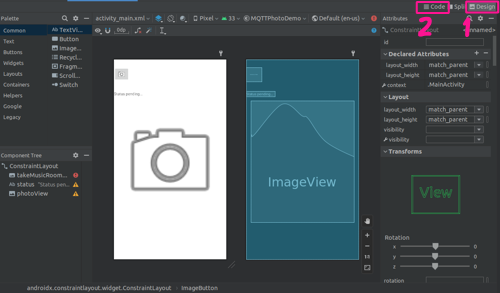
You can click on the Code view (2)
to return to the XML code.
Write the Android Java code
Paste the following code into MainActivity.java
below your package declaration:
package io.friedchips.android.mqttphotodemo;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.TextView;
import com.squareup.picasso.Picasso;
import org.eclipse.paho.android.service.MqttAndroidClient;
import org.eclipse.paho.client.mqttv3.IMqttActionListener;
import org.eclipse.paho.client.mqttv3.IMqttDeliveryToken;
import org.eclipse.paho.client.mqttv3.IMqttToken;
import org.eclipse.paho.client.mqttv3.MqttCallback;
import org.eclipse.paho.client.mqttv3.MqttClient;
import org.eclipse.paho.client.mqttv3.MqttConnectOptions;
import org.eclipse.paho.client.mqttv3.MqttException;
import org.eclipse.paho.client.mqttv3.MqttMessage;
import org.json.JSONObject;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
protected static final String TAG = "MQTTPhotoDemo"; // ID for logging purposes
protected static final String MQTT_SERVER_URL = "ssl://xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxs1.eu.hivemq.cloud:8883";
protected static final String MQTT_USER = "your user";
protected static final String MQTT_PWD = "your password";
protected static final String MQTT_TAKE_PHOTO_TOPIC = "yourTopics/takePhoto";
protected static final String MQTT_PHOTO_TAKEN_TOPIC = "ourTopics/photoTaken";
protected static int QOS = 2;
protected static final String REQUESTOR_ID_KEY = "requestorId";
protected static final String CLIENT_ID = "myAndroidPhone"; // will be included in incoming messages; indicates whether this device requested a photo
protected static final String SENSOR_ID_KEY = "sensorId";
protected static final String PHOTO_URL_KEY = "photo";
MqttAndroidClient mqttClient;
MqttConnectOptions mqttConnectionOptions;
ImageView photoView;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
photoView = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.photoView);
connectMQTT();
}
public void connectMQTT(){
mqttConnectionOptions = new MqttConnectOptions();
mqttConnectionOptions.setUserName(MQTT_USER);
mqttConnectionOptions.setPassword(MQTT_PWD.toCharArray());
String clientId = MqttClient.generateClientId();
mqttClient = new MqttAndroidClient(this.getApplicationContext(), MQTT_SERVER_URL, clientId);
try {
IMqttToken token = mqttClient.connect(mqttConnectionOptions);
token.setActionCallback(new IMqttActionListener() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(IMqttToken asyncActionToken) {
Log.d(TAG, "Connected to " + MQTT_SERVER_URL);
try {
subscribe(MQTT_PHOTO_TAKEN_TOPIC);
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e(TAG, "subscribe() failed");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void onFailure(IMqttToken asyncActionToken, Throwable exception) {
Log.d(TAG, "Couldn't connect to " + MQTT_SERVER_URL);
Log.e(TAG, "reason: ", exception);
}
});
} catch (MqttException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void subscribe(String topic) throws MqttException {
if(mqttClient.isConnected()){
Log.d(TAG, "subscribing to " + topic + "...");
mqttClient.subscribe(MQTT_PHOTO_TAKEN_TOPIC, QOS);
mqttClient.setCallback(new MqttCallback() {
@Override
public void connectionLost(Throwable cause) {
Log.e(TAG, "Connection lost during callback()", cause);
Log.i(TAG, "reconnecting...");
updateStatus("reconnecting...");
connectMQTT();
}
@Override
public void messageArrived(String topic, MqttMessage msg) throws Exception {
Log.d(TAG, "Received message from " + topic);
JSONObject json = new JSONObject(new String(msg.getPayload()));
final String sensorId = json.getString(SENSOR_ID_KEY);
final String requestorId = json.getString(REQUESTOR_ID_KEY);
final String photoURL = json.getString(PHOTO_URL_KEY);
Log.d(TAG, "sensorId = " + sensorId);
Log.d(TAG, "requestorId = " + requestorId);
Log.d(TAG, "photoURL = " + photoURL);
if(!CLIENT_ID.equals(requestorId) && !"".equals(requestorId)){
Log.d(TAG, "Photo requested by some other device.");
return;
}
// else..
Log.d(TAG, new String(msg.getPayload()));
Picasso.get()
.load(photoURL)
.into(photoView);
updateStatus("Photo sent (sensor ID: " + sensorId + ")");
}
@Override
public void deliveryComplete(IMqttDeliveryToken token) {;}
}
);
}
else{
Log.d(TAG, "NOT connected!!!!!!");
}
}
public void publish(final String topic, final String payload){
if(!mqttClient.isConnected()){
Log.w(TAG, "not connected during publish(). reconnecting...");
updateStatus("reconnecting...");
connectMQTT();
}
byte[] bytes = new byte[0];
try {
bytes = payload.getBytes("UTF-8");
MqttMessage message = new MqttMessage(bytes);
message.setQos(QOS);
mqttClient.publish(topic, message);
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException | MqttException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Log.d(TAG, "published to " + topic);
}
public void takePhoto(View view){
Log.d(TAG, "takePhoto() ");
String sensorId = (String) view.getTag(); // This value comes from the Button component in activity_main.xml
Log.d(TAG, "sensor ID " + sensorId);
updateStatus("Taking photo (sensor ID: " + sensorId + ")...");
String json = "{\"" + SENSOR_ID_KEY + "\":\"" + sensorId + "\", \"" + REQUESTOR_ID_KEY + "\":\"" + CLIENT_ID + "\"}";
publish(MQTT_TAKE_PHOTO_TOPIC, json);
}
public void updateStatus(final String s){
((TextView)findViewById(R.id.status)).setText(s);
}
}
The Code Explained
In a nutshell: the Android code sets up the
MQTT connection, subscribes to the photoTaken
topic that the ESP32 will publish to, calls the
Picasso library to download the photo by HTTP and
display it in our PhotoView
widget.
Constant Parameters
| Constant | value | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| MQTT_SERVER_URL | The URL of your MQTT server | |
| MQTT_USER | Your MQTT user name | |
| MQTT_PWD | Your MQTT password | |
| MQTT_TAKE_PHOTO_TOPIC | yourtopics/takePhoto | Must match the topic specified in your ESP32 code exactly |
| MQTT_PHOTO_TAKEN_TOPIC | yourtopics/photoTaken | Must match the topic specified in your ESP32 code exactly |
| CLIENT_ID | An identifier for this mobile phone | Should be unique if you are using multiple phones. If it's shared by several devices, each will spontaneously receive photos triggered by the others. |
Android Code Logic
Here's what the Android code does:
- The
android:onClick="takePhoto"property of the button in activity_main.xml calls thetakePhoto()method. -
The
takePhoto()method first generates the JSON payload of the MQTT message, including:- The ID of ESP32 Cam we want to talk
to (specified by the button's
android:tagin the activity_main.xml file) - The ID of the mobile phone (which will be returned to us from the ESP32 after the photo has been taken)
- Your MQTT server client ID
It then calls the
publish()method. - The ID of ESP32 Cam we want to talk
to (specified by the button's
-
The
publish()method publishes the JSON message to the MQTT takePhoto topic.When the ESP32 Cam receives the message (assuming its sensorID matches) it will take a photo, upload it and notify us of the URL of the photo.
Test in Android Studio Emulator
This involves running our app on a virtual device in Android Studio.
Install an Android Emulator
If you haven't got a virtual device installed, follow these steps. If you've already got one installed, skip ahead to the testing step.
- From the Device dropdown in the top right of the screen select Device Manager. The device manager window will open with the Virtual option selected by default.
- Hit Create Device.
- Select a phone model (any one will do for this demo) in the Select Hardware dialogue and click Next.
- Select a system image from the next dialogue (ideally with target Android 11 or higher), wait for it to download and click Finish.
Your selected device will now appear in the Device Manager window and will be present in the Available Devices dropdown.
Launch Android Device Emulator
Select your device from the Available Devices dropdown (1) and hit the Run icon (2).
The virtual phone will appear in the Emulator window.
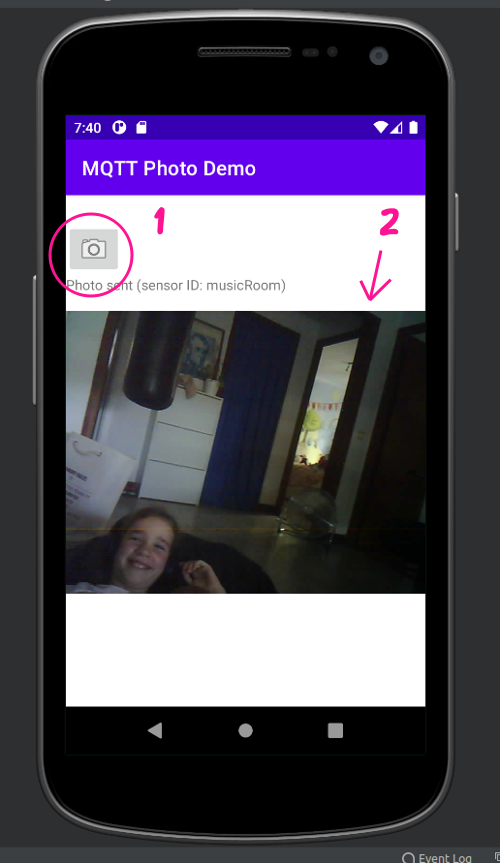
With the ESP32 Cam powered up (and pointing at something interesting), click the take photo button (1) in the emulator.
A photo will appear in the ImageView widget (2) :)
Deploy Android App to Phone
First, make sure the ESP32 Cam chip is connected via
the USB lead to your PC and that Allow USB debugging
is enabled
If you haven't connected your Android phone to your PC
before go to Settings >
System and tap on Build Number seven
times. This will activate the Developer Options
menu. Then go to Settings >
Developer Options and click on Enable
USB Debugging.
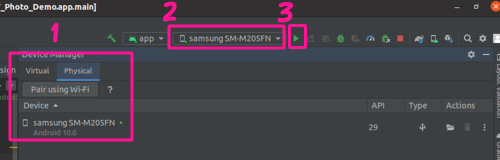
Your actual phone will now be available in the Available Devices dropdown (and in the Device Manager under the Physical tab).
With your phone selected in the Available Devices dropdown, hit the Run icon. This will install your app together with an icon on your phone and launch it.
After this you can disconnect your phone from the PC and simply tap the icon to start the app any time you like.
Take a Photo from your Phone using MQTT!
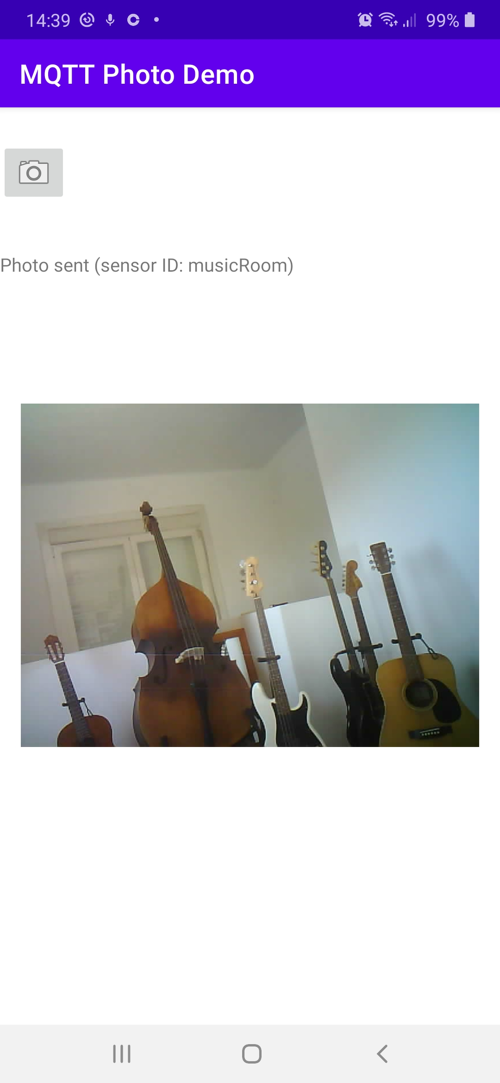
Open the app on your phone by tapping the new icon and tap the take photo button. A photo from the ESP32 Cam will be displayed.

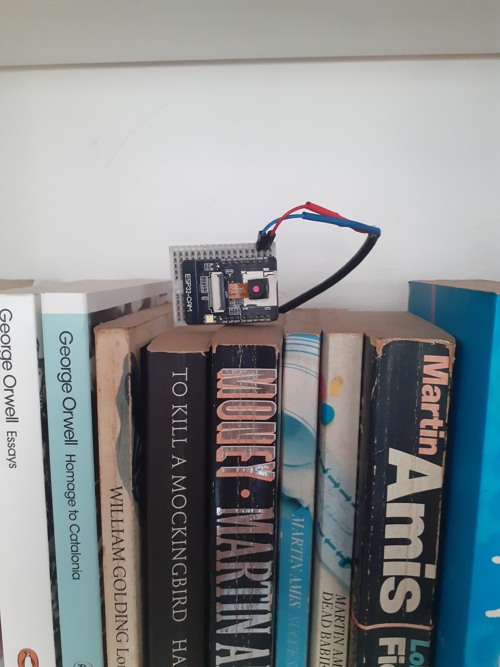
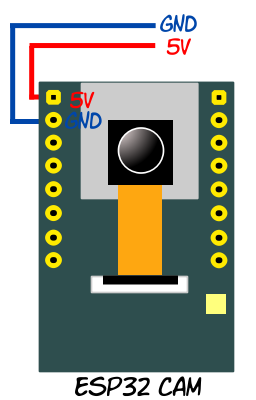
Note that the ESP32 Cam does not need to be connected to your PC. It just needs to be powered up (by a 5v battery, for example) and in range of the wifi router you configured. This is the whole point of IoT.
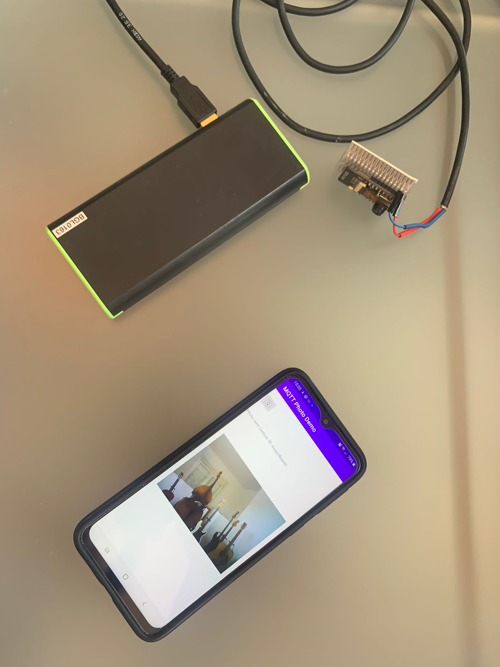


Enjoy!!!